Obstetric Ultrasound
- Home>
- Obstetric Ultrasound
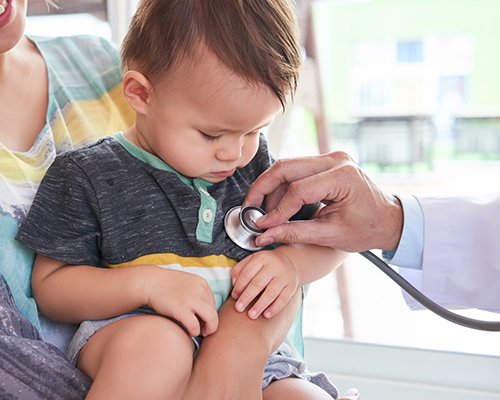
Ultrasound examinations are painless and easily tolerated by most patients.
However, at times during an obstetrical ultrasound, the sonographer may have to press more firmly to get closer to the embryo or fetus to visualize the structure better. Any discomfort is usually minimal and temporary.
At times the sonographer may have to press more firmly to get closer to the embryo or fetus to visualize the structure better. Any discomfort is usually minimal and temporary. If a Doppler ultrasound study is performed, you may actually hear pulse-like sounds that change in pitch as the blood flow is monitored and measured.
With transvaginal scanning, there may be minimal discomfort as the transducer is inserted into the vagina.
This ultrasound examination is usually completed within 30 minutes.
When the examination is complete, you may be asked to dress and wait while the ultrasound images are reviewed.
After an ultrasound examination, you should be able to resume your normal activities immediately.
Detailed MR images allow physicians to evaluate various parts of the body and determine the presence of certain diseases.
However, at times during an obstetrical ultrasound, the sonographer may have to press more firmly to get closer to the embryo or fetus to visualize the structure better. Any discomfort is usually minimal and temporary.
At times the sonographer may have to press more firmly to get closer to the embryo or fetus to visualize the structure better. Any discomfort is usually minimal and temporary. If a Doppler ultrasound study is performed, you may actually hear pulse-like sounds that change in pitch as the blood flow is monitored and measured.
With transvaginal scanning, there may be minimal discomfort as the transducer is inserted into the vagina.
This ultrasound examination is usually completed within 30 minutes.
When the examination is complete, you may be asked to dress and wait while the ultrasound images are reviewed.
After an ultrasound examination, you should be able to resume your normal activities immediately.
Detailed MR images allow physicians to evaluate various parts of the body and determine the presence of certain diseases.
Ultrasound is safe and painless, and produces pictures of the inside of the body using sound waves. Ultrasound imaging, also called ultrasound scanning or sonography, involves the use of a small transducer (probe) and ultrasound gel placed directly on the skin. High-frequency sound waves are transmitted from the probe through the gel into the body. The transducer collects the sounds that bounce back and a computer then uses those sound waves to create an image. Ultrasound examinations do not use ionizing radiation (as used in x-rays), thus there is no radiation exposure to the patient. Because ultrasound images are captured in real-time, they can show the structure and movement of the body's internal organs, as well as blood flowing through blood vessels.
Ultrasound imaging is a noninvasive medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions.
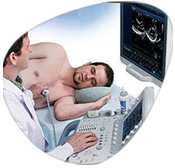
Obstetrical ultrasound provides pictures of an embryo or fetus within a woman's uterus, as well as the mother's uterus and ovaries.
A Doppler ultrasound study may be part of an obstetrical ultrasound examination.
Doppler ultrasound is a special ultrasound technique that evaluates blood flow through a blood vessel, including the body's major arteries and veins in the abdomen, arms, legs, neck and head (in infants and children).
During an obstetrical ultrasound the examiner may evaluate blood flow in the umbilical cord or may, in some cases, assess blood flow in the fetus or placenta.
Ultrasound imaging is a noninvasive medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions.
Obstetrical ultrasound provides pictures of an embryo or fetus within a woman's uterus, as well as the mother's uterus and ovaries.
A Doppler ultrasound study may be part of an obstetrical ultrasound examination.
Doppler ultrasound is a special ultrasound technique that evaluates blood flow through a blood vessel, including the body's major arteries and veins in the abdomen, arms, legs, neck and head (in infants and children).
During an obstetrical ultrasound the examiner may evaluate blood flow in the umbilical cord or may, in some cases, assess blood flow in the fetus or placenta.
You should wear a loose-fitting, two-piece outfit for the examination. Only the lower abdominal area needs to be exposed during this procedure.
The radiologist or sonographer may elect to examine an early pregnancy by means of transvaginal ultrasound in order to see the pregnancy more closely or to assess the cervix. For more information on transvaginal ultrasound, see the Pelvic Ultrasound page.
The radiologist or sonographer may elect to examine an early pregnancy by means of transvaginal ultrasound in order to see the pregnancy more closely or to assess the cervix. For more information on transvaginal ultrasound, see the Pelvic Ultrasound page.
Other Guidlines