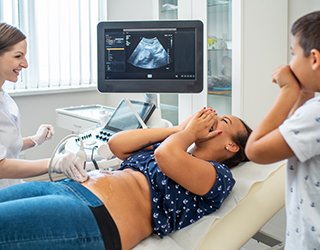
Ultrasound - Abdomen
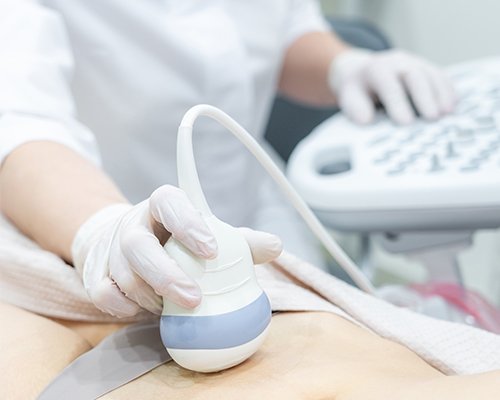

Ultrasound is safe and painless, and produces pictures of the inside of the body using sound waves. Ultrasound imaging, also called ultrasound scanning or sonography, involves the use of a small transducer (probe) and ultrasound gel placed directly on the skin. High-frequency sound waves are transmitted from the probe through the gel into the body.
The transducer collects the sounds that bounce back and a computer then uses those sound waves to create an image. Ultrasound examinations do not use ionizing radiation (as used in x-rays), thus there is no radiation exposure to the patient. Because ultrasound images are captured in real-time, they can show the structure and movement of the body's internal organs, as well as blood flowing through blood vessels.
Ultrasound imaging is a noninvasive medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions.
An abdominal ultrasound produces a picture of the organs and other structures in the upper abdomen.
A Doppler ultrasound study may be part of an abdominal ultrasound examination.
Doppler ultrasound is a special ultrasound technique that evaluates blood flow through a blood vessel, including the body's major arteries and veins in the abdomen, arms, legs, neck and head (in infants and children).
The transducer collects the sounds that bounce back and a computer then uses those sound waves to create an image. Ultrasound examinations do not use ionizing radiation (as used in x-rays), thus there is no radiation exposure to the patient. Because ultrasound images are captured in real-time, they can show the structure and movement of the body's internal organs, as well as blood flowing through blood vessels.
Ultrasound imaging is a noninvasive medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions.
An abdominal ultrasound produces a picture of the organs and other structures in the upper abdomen.
A Doppler ultrasound study may be part of an abdominal ultrasound examination.
Doppler ultrasound is a special ultrasound technique that evaluates blood flow through a blood vessel, including the body's major arteries and veins in the abdomen, arms, legs, neck and head (in infants and children).
You should wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing for your ultrasound exam. You may need to remove all clothing and jewelry in the area to be examined.
You may be asked to wear a gown during the procedure.
Preparations depend on the type of ultrasound you are having.
You may be asked to wear a gown during the procedure.
Preparations depend on the type of ultrasound you are having.
- For a study of the liver, gallbladder, spleen, and pancreas, you may be asked to eat a fat-free meal on the evening before the test and then to avoid eating for eight to 12 hours before the test.
- For ultrasound of the kidneys, you may be asked to drink four to six glasses of liquid about an hour before the test to fill your bladder. You may be asked to avoid eating for eight to 12 hours before the test to avoid gas buildup in the intestines.
- For ultrasound of the aorta, you may need to avoid eating for eight to 12 hours before the test.
Ultrasound examinations are painless and easily tolerated by most patients.
Abdominal ultrasound is usually completed within 30 minutes.
If a Doppler ultrasound study is performed, you may actually hear pulse-like sounds that change in pitch as the blood flow is monitored and measured.
When the examination is complete, you may be asked to dress and wait while the ultrasound images are reviewed.
After an ultrasound examination, you should be able to resume your normal activities immediately.
Abdominal ultrasound is usually completed within 30 minutes.
If a Doppler ultrasound study is performed, you may actually hear pulse-like sounds that change in pitch as the blood flow is monitored and measured.
When the examination is complete, you may be asked to dress and wait while the ultrasound images are reviewed.
After an ultrasound examination, you should be able to resume your normal activities immediately.
Other Guidlines